What is the CIA Triad?
Before we get into the details of how blockchain can improve information security, let’s talk about the CIA triad. No, not the government agency, but the one related to Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability.
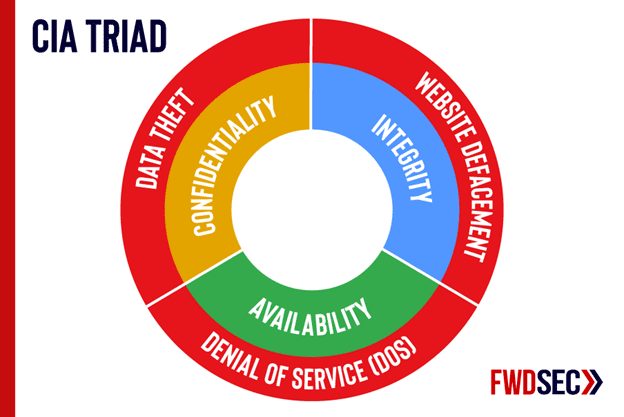
Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability are the key attributes when it comes to information security and determining the impact of an attack involving some data, as well as the controls required for its protection.
C – Confidentiality
Confidentiality is about keeping sensitive data inaccessible to unauthorized parties and is typically achieved through methods such as encryption, hashing, masking, or access control.
I – Integrity
Specifically, integrity is about assurance that data has not been modified by unauthorized parties. This can be achieved by using signatures or Message Authentication Codes (MAC).
A – Availability
Last but not least, availability is about having the data available at all times when required, and the resulting impact from lack of such availability. A Denial of Service (DoS) attack often impacts this attribute. Having back-ups, redundancy, and a disaster recovery plan can help mitigate threats that impact availability.
Each of these CIA attributes should be considered when assessing the impact of an attack on a given piece of information.
CIA in action
Let’s say you own a retail store and your address listed on your public website. Since this information is public, there is no confidentiality requirement or impact of exposure.
However, you do not want an unauthorized user to edit that address to direct your customers to a competitor. In this case, there would be a high level of impact to your business due to compromise of integrity of the address.
Availability is also a concern, since some of your customers who cannot find your address if your website is down may shop at an alternate store. However, this does not apply to all customers, some of which will visit your site at a later time and continue to shop with you. Based on this, the impact due to lack of availability is moderate.
How Blockchain impacts CIA
Now let’s talk about blockchain and how it helps reduce impact to each of the C, I, and A of the triad.
Blockchain is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger, which offers a high level of trust. The blockchain architecture does not have central control point.
You can think of it as a distributed database, where a full copy of the entire data set resides at each full-node across a network. Transactions are recorded in a verifiable and immutable manner and put in blocks. Data recorded in a given block cannot be altered afterwards without alteration of all subsequent blocks. Since a hash of each block is included in the next block, an attacker needs to modify all blocks and adjust all the hashes in the chain, making it nearly impossible due to high computational resource requirements.
As a result of the decentralized architecture, there are multiple copies of the blockchain that can be used for verification as well. Even if the attacker modifies all blocks of the chain in one node, consensus will be required by majority of the nodes to accept this modified version, meaning the attacker would need to control the majority. Using a decentralized and immutable ledger, there is no need for a central trust authority to verify and validate transactions.
So how does blockchain impact Information Security’s CIA-triad?
Integrity – since all data stored as transactions in the blocks are signed, it provides a high level of integrity protection. As mentioned, changes to the data in a block are also nearly impossible due to the use of linking via hashes, and the consensus requirement.
Availability – since a distributed architecture is used, a full copy of the data resides across several nodes. This provides a high level of Availability.
Confidentiality – since blockchain requires transaction data to be visible and verifiable, it has low confidentiality.
- With public blockchains, confidentiality may be of concern since all participating nodes can read this data. If a high level of confidentiality is required, the system needs to provide additional protection such as application-level encryption, tokenization, or other means where sensitive data is not directly readable by unauthorized parties.
- Private blockchains, on the other hand, can help address confidentiality requirements since access control is enforced to limit access to specific users for specific transactions.
Further Considerations
It should be noted that the size of the network is important since if data is not well distributed, it may be vulnerable to attacks.
In addition, where there are requirements for data to be deleted (such as GDPR), consideration should be given to render the data useless if required since blockchain does not provide the ability to delete transactions.
In summary, use of blockchain can improve information security with respect to Integrity and Availability, while also allowing for Confidentiality of sensitive data if required using custom solutions.
As with any technology, there is no single solution that solves all problems and where trust, integrity, and availability are top concerns blockchain is a great choice to reduce the related impact.
How Mature is Your DevSecOps?
Our comprehensive DevSecOps Maturity Assessment covers 8 key phases of DevSecOps practices, 29 questions in total.
By evaluating your team on each capability, you can determine if your DevSecOps maturity level is early, intermediate, or advanced. Your assessment includes a custom report that provides your overall maturity as well as detailed recommendations you can take to enhance your security posture.



